This month, we’re diving deep into the dazzling world of lab-grown diamonds. Once considered a futuristic novelty, they’re now a sparkling reality, revolutionising the jewellery industry.
What are Lab-Grown Diamonds?
How Are They Made?
There are two primary methods for creating lab-grown diamonds:
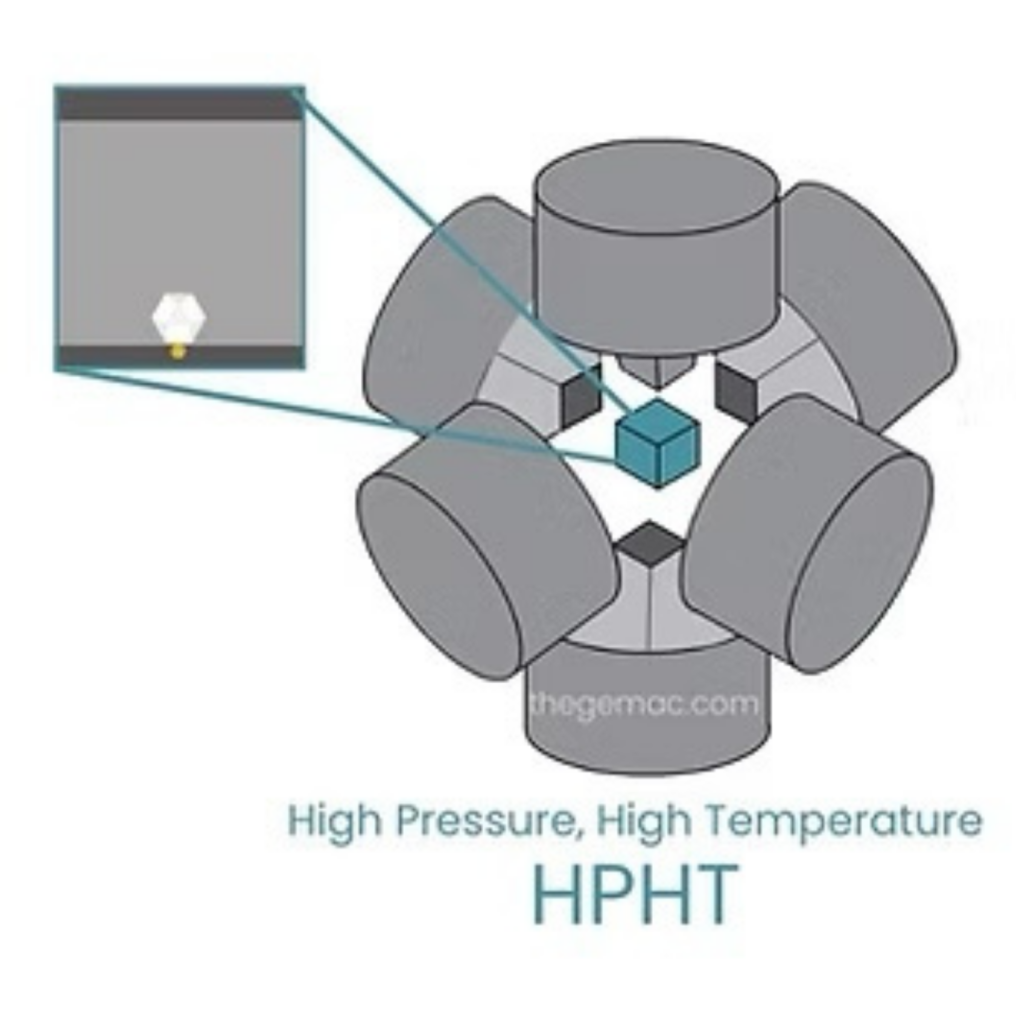
High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) Process: The HPHT process mimics the extreme conditions found in the Earth’s mantle. It applies pressures of around 5 GPa (50,000 atmospheres) and temperatures of approximately 1,500°C to carbon sources. It takes about a fortnight to grow a 1-carat diamond using the HPHT method. This process accounts for about 20% of the lab-grown diamond market.
Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD) Process: In the CVD process, a carbon-rich gas, such as methane (CH4), is introduced into a vacuum chamber. The gas is then ionised, creating a plasma that deposits carbon atoms onto a substrate. CVD is responsible for about 80% of lab-grown diamonds.

The Benefits of Lab-Grown Diamonds

Addressing Common Misconceptions:

De Beers natural diamonds hoax:

Origins of the hoax: The De Beers diamond hoax began in the early 20th century when De Beers, facing a decline in diamond demand, sought to create artificial scarcity and elevate the perceived value of diamonds through strategic marketing efforts.

The “A Diamond is Forever” campaign: Launched in 1947, this iconic campaign linked diamonds to love and commitment, promoting the idea that a diamond engagement ring was essential for marriage proposals. This messaging significantly influenced consumer behaviour.

Increased demand: The campaign dramatically increased the percentage of brides receiving diamond engagement rings, from about 10% in the 1930s to over 80% by the end of the 20th century, solidifying diamonds as a cultural norm.
Market control and high prices: By controlling the supply of diamonds and creating an artificial demand, De Beers maintained high prices and significant profits, effectively monopolizing the diamond trade for decades.

Ethical concerns: The hoax has faced criticism for market manipulation, including accusations of dealing in conflict diamonds linked to human rights abuses and environmental degradation from diamond mining practices.

Cultural impact: The De Beers diamond hoax not only reshaped consumer perceptions of diamonds but also inspired similar marketing strategies across various industries, highlighting the power of advertising in creating demand for products.
Market Opportunity
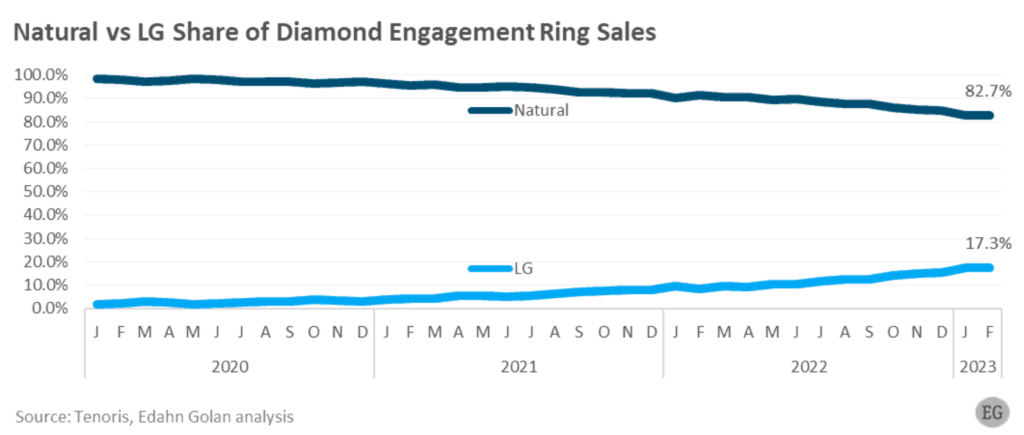
Lab grown diamonds market:
- The lab-grown diamond market currently valued at approximately $22 billion, presents significant growth potential, especially when considering the overall natural diamond market, which is estimated at $100 billion.
- Loose lab-grown diamond unit sales in the U.S. held a share of 13.7% in 2020, which was viewed as relatively high at the time. Since then, their share has increased to a remarkable 46.6% as of February 2023. In just three years, lab-grown diamonds moved from just above a tenth of total sales to nearly half. A similar trend is expected to replicate in India.
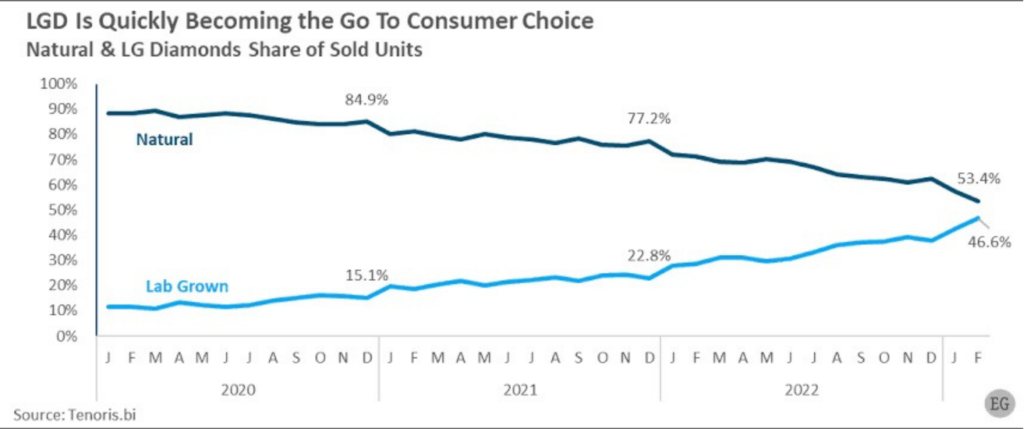
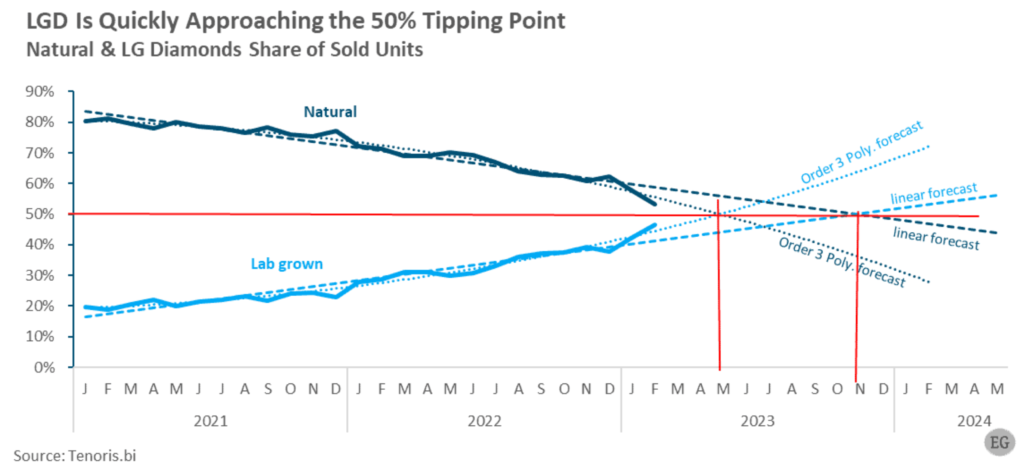
LGD jewellery opportunity
- India’s lab grown diamond jewellery market was valued at US$
264.5 million in 2022. Over the next ten years, lab grown diamond jewellery sales is expected to rise at 14.8% CAGR. Total market size is expected to increase from $300 million in 2023 to $1.2 billion by 2033. - Lab-grown diamond (LGD) jewellery is poised to capitalize on significant opportunities within the $22 billion bridal jewellery market and the $32 billion gifting jewellery market of India.
- Govt. of India has shown big support to the Lab Grown Diamond industry by promoting sustainability with our PM Narendra Modi gifting a 7.5 carats LGD to Joe Biden’s wife.
Government initiatives
- A grant from the Indian government to IIT: The Indian government has given a grant of INR 242 crores to IIT Madras to study lab-created diamonds. The government has approved the investment, which would be made over five years.
- Removal of 5% custom duty on diamond seeds: The government has eliminated the 5% customs duty formerly applied to the seeds used to create rough lab-made diamonds.
- Removal of the term “synthetic”: The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Gemmological Institute of India (GIA) banned the use of the term “synthetic” in reference to lab created diamonds. Because lab diamonds share the same optical, physical, thermal, and chemical characteristics as natural diamonds, these two institutions now designate them as such.
- Different import codes for lab-grown diamonds and natural diamonds: Previously, whether they were man-made diamonds or natural stones, all raw synthetic gemstones imported into India had the same import code: 71042000. But now, rough lab-grown diamonds are classified as 71042010, while other rough synthetic stones are given the designation 71042090. This will help track and monitor the two types of diamonds.
Growth drivers:
Increasing aspirational buyers: As lab grown diamond brands offer competitively priced lab-grown diamond jewellery, it taps into the aspirations of middle-class consumers to own diamonds. This positions the brand for sustained success by making diamond ownership an attainable goal for a wider demographic of value-conscious consumer with growing spending power.
Increasing cost related awareness: As consumer awareness of lab-grown diamonds continues to rise, the LGD brands are well- positioned to attract new customers. The shift in consumer preferences towards sustainable and cost-effective jewellery options presents a timely opportunity for growth.
Potential for High Returns: With the rapid expansion of the lab- grown diamond market and the increasing spending power of the emerging middle class, we as investors can expect substantial returns as the new age LGD brandscapture market share in this burgeoning industry.
What to Look for When Buying:
- Certification: Ensure your lab-grown diamond is certified by reputable gemmological laboratories like the GIA or IGI.
- The 4Cs: Just like mined diamonds, lab-grown diamonds are graded based on the 4Cs: Cut, Clarity, Colour, and Carat.
- Retailer Reputation: Choose a reputable jeweller who is transparent about their lab-grown diamond sourcing and knowledgeable about their products.
From the Managing Partner's desk